iOS에서 위치 테스트 시 번거로운 점
- 안드로이드와 달리 Fake GPS 사용이 불가하기 때문에 실제로 발품을 팔아야함
- 실시간 로그를 볼 수 없기 때문에 문제 발생 시 원인 파악이 어렵다
- 사소한 수정이 발생해도 빌드 후 다시 발품을 팔아야함
하여 실제 단말기에서는 방법은 없었지만 시뮬레이터에서 가상 위치로 테스트할 수 있는 방법을 공유드립니다.
하기 예제는 애플 공식 문서를 참고하여 지오펜싱(Geofencing : 지리와 울타리의 합성어)으로 준비하였습니다.
1. 위치 서비스 코드 작성
1-1. Project - Signing & Capabilities

위치 사용을 위해 Background Modes 추가 후 Location updates 항목을 체크해주세요.
1-2. Info.plist
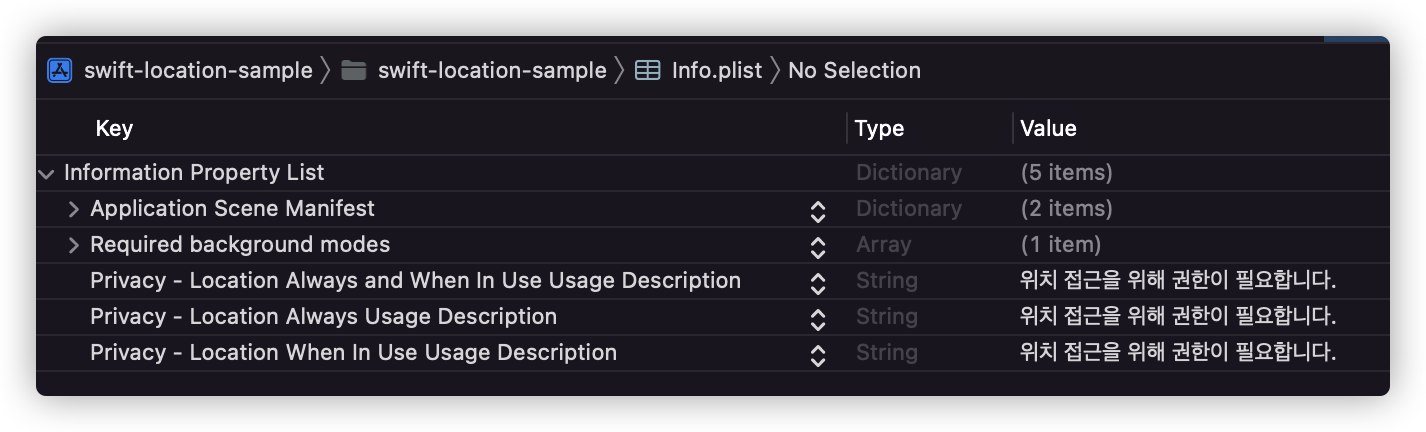
위치 권한 팝업에 들어갈 내용을 추가해주었습니다.
1-3. 코드 작성
import Foundation
import CoreLocation
class LocationService: NSObject {
static let shared = LocationService()
private override init() {
super.init()
locationManager = CLLocationManager()
locationManager.delegate = self
}
var locationManager: CLLocationManager!
}
extension LocationService {
func registLocation() {
let location = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.4967867, longitude: 126.9978993)
let region = CLCircularRegion(center: location,
radius: 1.0,
identifier: "id")
region.notifyOnEntry = true
region.notifyOnExit = true
locationManager.allowsBackgroundLocationUpdates = true
locationManager.pausesLocationUpdatesAutomatically = false
locationManager.startUpdatingLocation()
locationManager.startMonitoring(for: region)
print("region regist: \(region)")
}
}
extension LocationService: CLLocationManagerDelegate {
func requestAlwaysLocation() {
switch locationManager.authorizationStatus {
case .notDetermined:
locationManager.requestAlwaysAuthorization()
case .authorizedWhenInUse:
locationManager.requestAlwaysAuthorization()
case .authorizedAlways:
registLocation()
default:
print("Location is not avaiable.")
}
}
func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didStartMonitoringFor region: CLRegion) {
print("didStartMonitoringFor")
}
func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didDetermineState state: CLRegionState, for region: CLRegion) {
switch state {
case .inside:
print("들어왔습니다.")
case .outside:
print("나왔습니다.")
case .unknown: break
// do not something
}
}
}위치 서비스를 관리하는 LocationService 클래스를 싱글톤으로 작성하였습니다.
- CLLocationManager
startMonitoring: 설정한 지역(region)을 모니터링합니다.- 모니터링 결과는
didDetermineStateDelegate로 들어오게 됩니다(outside, inside)
- 모니터링 결과는
- CLCircularRegion
center: 중심이 될 좌표를 설정합니다 (위/경도)radius: 중심으로부터 반경이 될 거리를 설정합니다(m 단위)identifier: 해당 리전의 id를 등록합니다.
2. 호출
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
let ls = LocationService.shared
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
ls.requestAlwaysLocation()
}
}Region을 등록할 페이지에서 requestAlwaysLocation 함수를 호출하여 region을 등록하였습니다.
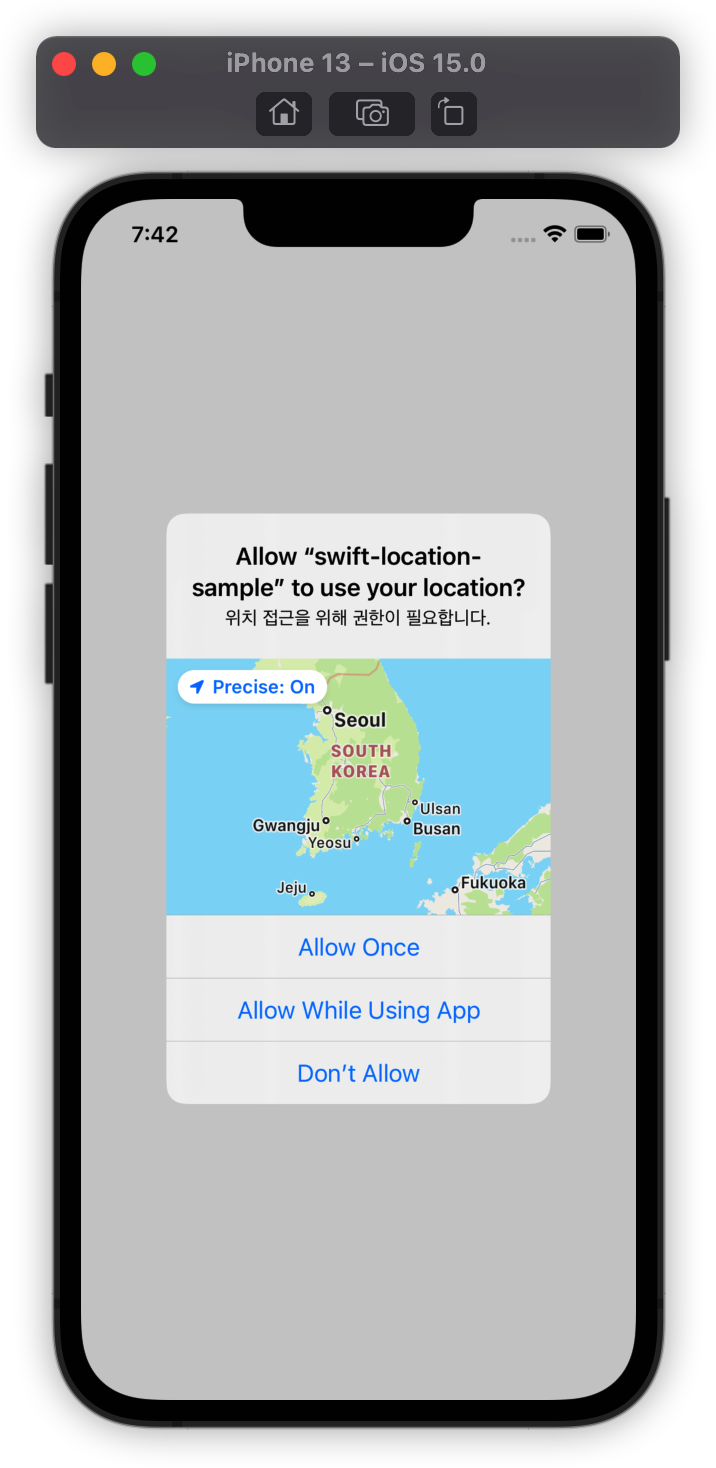
이제 앱을 실행하면 앱에서 위치를 사용할 것인지 묻는 화면이 나옵니다. 사용할거니까 당연히 사용을 선택해줍니다.
region regist: CLCircularRegion (identifier:'id', center:<+37.49678670,+126.99789930>, radius:1.00m)
로그를 보면 위에 작성해둔 위치가 등록되었음을 알 수 있습니다.
3. 테스트
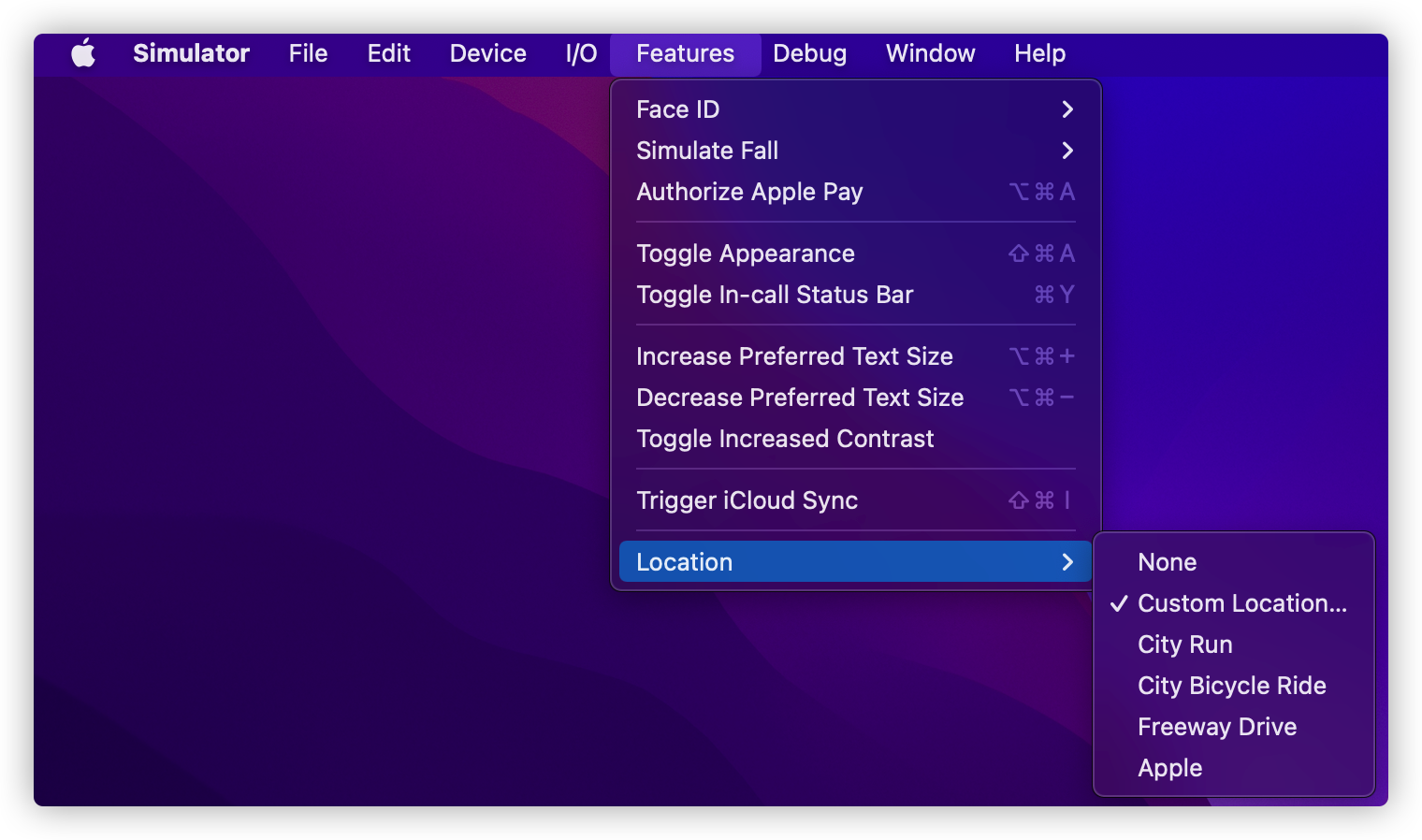
Simulator - Features - Location 항목으로 이동하면 시뮬레이터의 위치를 변경할 수 있습니다.

위치를 Apple(캘리포니아)로 변경하면 didDetermineState가 outside로 들어오고
Custom Location(코드상 등록했던 위치)로 변경하면 didDetermineState가 inside로 들어오는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
4. 앱이 꺼진 상태에서의 지오펜싱
모니터링을 등록해놓으면 앱이 꺼져있어도 in/out 이벤트를 받아서 처리할 수 있습니다.
이를 테스트 하기 위해 Local Notification을 이용하였습니다.
AppDelegate - 푸시 알림 권한 설정
import UIKit
import CoreData
import UserNotifications
@main
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
// Override point for customization after application launch.
let center = UNUserNotificationCenter.current();
center.delegate = self
if #available(iOS 10, *) {
center.requestAuthorization(options:[.badge, .alert, .sound]){ (granted, error) in }
application.registerForRemoteNotifications()
}
return true
}
// MARK: UISceneSession Lifecycle
func application(_ application: UIApplication, configurationForConnecting connectingSceneSession: UISceneSession, options: UIScene.ConnectionOptions) -> UISceneConfiguration {
// Called when a new scene session is being created.
// Use this method to select a configuration to create the new scene with.
return UISceneConfiguration(name: "Default Configuration", sessionRole: connectingSceneSession.role)
}
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didDiscardSceneSessions sceneSessions: Set<UISceneSession>) {
// Called when the user discards a scene session.
// If any sessions were discarded while the application was not running, this will be called shortly after application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions.
// Use this method to release any resources that were specific to the discarded scenes, as they will not return.
}
// MARK: - Core Data stack
lazy var persistentContainer: NSPersistentContainer = {
/*
The persistent container for the application. This implementation
creates and returns a container, having loaded the store for the
application to it. This property is optional since there are legitimate
error conditions that could cause the creation of the store to fail.
*/
let container = NSPersistentContainer(name: "swift_location_sample")
container.loadPersistentStores(completionHandler: { (storeDescription, error) in
if let error = error as NSError? {
// Replace this implementation with code to handle the error appropriately.
// fatalError() causes the application to generate a crash log and terminate. You should not use this function in a shipping application, although it may be useful during development.
/*
Typical reasons for an error here include:
* The parent directory does not exist, cannot be created, or disallows writing.
* The persistent store is not accessible, due to permissions or data protection when the device is locked.
* The device is out of space.
* The store could not be migrated to the current model version.
Check the error message to determine what the actual problem was.
*/
fatalError("Unresolved error \(error), \(error.userInfo)")
}
})
return container
}()
// MARK: - Core Data Saving support
func saveContext () {
let context = persistentContainer.viewContext
if context.hasChanges {
do {
try context.save()
} catch {
// Replace this implementation with code to handle the error appropriately.
// fatalError() causes the application to generate a crash log and terminate. You should not use this function in a shipping application, although it may be useful during development.
let nserror = error as NSError
fatalError("Unresolved error \(nserror), \(nserror.userInfo)")
}
}
}
}
extension AppDelegate: UNUserNotificationCenterDelegate {
func userNotificationCenter(_ center: UNUserNotificationCenter, willPresent notification: UNNotification, withCompletionHandler completionHandler: @escaping (UNNotificationPresentationOptions) -> Void) {
completionHandler([.badge, .alert, .sound])
}
func userNotificationCenter(_ center: UNUserNotificationCenter, didReceive response: UNNotificationResponse, withCompletionHandler completionHandler: @escaping () -> Void) {
}
}
LocationService - Local Notification 작업
//
// LocationService.swift
// swift-location-sample
//
// Created by ycsong on 2021/12/27.
//
import Foundation
import CoreLocation
import NotificationCenter
class LocationService: NSObject {
static let shared = LocationService()
private override init() {
super.init()
locationManager = CLLocationManager()
locationManager.delegate = self
}
var locationManager: CLLocationManager!
}
extension LocationService {
func fireNotification(_ title: String = "Background Test", body: String) {
let notificationCenter = UNUserNotificationCenter.current()
notificationCenter.getNotificationSettings { (settings) in
if settings.alertSetting == .enabled {
let content = UNMutableNotificationContent()
content.title = title
content.body = body
let uuidString = UUID().uuidString
let trigger = UNTimeIntervalNotificationTrigger(timeInterval: 1, repeats: false)
let request = UNNotificationRequest(identifier: "Test-\(uuidString)", content: content, trigger: trigger)
notificationCenter.add(request, withCompletionHandler: { (error) in
if error != nil {
// Handle the error
}
})
}
}
}
}
extension LocationService {
func registLocation() {
let location = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 37.4967867, longitude: 126.9978993)
let region = CLCircularRegion(center: location,
radius: 1.0,
identifier: "id")
region.notifyOnEntry = true
region.notifyOnExit = true
locationManager.allowsBackgroundLocationUpdates = true
locationManager.pausesLocationUpdatesAutomatically = false
locationManager.startUpdatingLocation()
locationManager.startMonitoring(for: region)
print("region regist: \(region)")
}
}
extension LocationService: CLLocationManagerDelegate {
func requestAlwaysLocation() {
switch locationManager.authorizationStatus {
case .notDetermined:
locationManager.requestAlwaysAuthorization()
case .authorizedWhenInUse:
locationManager.requestAlwaysAuthorization()
case .authorizedAlways:
registLocation()
default:
print("Location is not avaiable.")
}
}
func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didDetermineState state: CLRegionState, for region: CLRegion) {
switch state {
case .inside:
fireNotification("Inside", body: "들어왔습니다.")
case .outside:
fireNotification("Outside", body: "나왔습니다.")
case .unknown: break
// do not something
}
}
}


5. 소스코드
전체 코드를 깃허브에 업로드해두었습니다.
https://github.com/YuchanSong/swift-location-sample
GitHub - YuchanSong/swift-location-sample: 시뮬레이터 위치 테스트
시뮬레이터 위치 테스트. Contribute to YuchanSong/swift-location-sample development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com

